lv filling pressures | left ventricular filling pressure chart lv filling pressures Figure 1 shows the algorithm recommended by the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) to evaluate LVFP.2 Importantly, the recommendations advocate careful consideration of all available clinical, 2D, and Doppler data to . See more 4.7 out of 5 based on 35,731 reviews. Find the perfect pre-owned Rolex Submariner at Watchfinder & Co. Trusted by thousands, with free delivery and 24-month warranty. .
0 · raised Lv filling pressures
1 · left ventricular filling pressure chart
2 · increased left ventricular filling pressure
3 · increased Lv filling pressure
4 · elevated left ventricular filling pressures
5 · elevated left sided filling pressures
6 · elevated Lv filling pressures
7 · Lv filling pressure normal range
This is the new Omega Seamaster 300. It has the same old school charm, and the same blue and black dial variants, only it's been brought closer to the original, both in spirit and aesthetic. While the new .
Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) plays a key role in the pathophysiology of heart failure (HF). It is caused by impaired left ventricular (LV) relaxation with or without reduced restoring forces and increased Lv chamber stiffness leading to the inability of the ventricle to fill adequately . See moreLeft ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, . See more
Identification of elevated LVFP at rest or during exercise is pivotal for the diagnosis of HFpEF, which gained additional interest since medical . See moreA number of echocardiographic parameters may be used to differentiate between normal and elevated LVFP. All the recommended . See moreFigure 1 shows the algorithm recommended by the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) to evaluate LVFP.2 Importantly, the recommendations advocate careful consideration of all available clinical, 2D, and Doppler data to . See more
Results: Mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 47%, with 209 patients having an LVEF <50%. Invasive measurements showed elevated LV filling pressure in 58% of patients.ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic . Echocardiography is widely used to evaluate left ventricular (LV) diastolic function in patients suspected of heart failure. For patients in sinus rhythm, a combination of several . Left ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, there is typically elevated LVFP at rest, and in some cases only during exercise.
Results: Mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 47%, with 209 patients having an LVEF <50%. Invasive measurements showed elevated LV filling pressure in 58% of patients.ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B).
Echocardiography is widely used to evaluate left ventricular (LV) diastolic function in patients suspected of heart failure. For patients in sinus rhythm, a combination of several echocardiographic parameters can differentiate between normal and elevated LV filling pressure with good accuracy.In patients with heart failure and reduced EF (HFrEF), the main goal is to estimate LV filling pressures and grade the degree of diastolic dysfunction (diastolic dysfunction is presumed to be present in these patients) based on the parameters presented below and . This guideline outlines a structured approach to the assessment of diastolic function and includes recommendations for the assessment of LV relaxation and filling pressures. Non-routine echocardiographic measures are described alongside guidance for application in .
The term left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP) refers to the LV pressures during diastole. They are illustrated in Fig. 13.3 and include LV minimal pressure, pre-A wave pressure, and LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is a condition of impaired LV relaxation and increased LV chamber stiffness, which can lead to elevated LV filling pressures. This topic summarizes available echocardiographic methods for assessment of LV diastolic function.
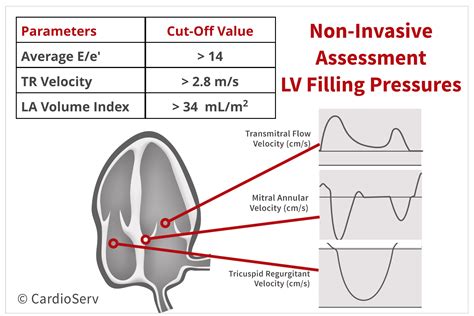
Values for average E/e′ ratio < 8 usually indicate normal LV filling pressures, values > 14 have high specificity for increased LV filling pressures. E/e′ ratio is not accurate in normal subjects, patients with heavy annular calcification, mitral valve and pericardial disease.LVEDP is the highest of all filling pressures and has its own Doppler correlates. In patients with diastolic dysfunction, LVEDP is the earliest pressure to become abnormally elevated. Exercise, pacing-induced tachycardia, and increased afterload can elucidate the abnormalities in LV diastolic function, when there are equivocal findings at rest. Left ventricular filling pressure is the pressure that fills the ventricle in diastole and determines stroke volume according to the Frank-Starling mechanism. In patients with HF, there is typically elevated LVFP at rest, and in some cases only during exercise.
raised Lv filling pressures
Results: Mean left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 47%, with 209 patients having an LVEF <50%. Invasive measurements showed elevated LV filling pressure in 58% of patients.ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B).
gucci guilty perfume sgop
Echocardiography is widely used to evaluate left ventricular (LV) diastolic function in patients suspected of heart failure. For patients in sinus rhythm, a combination of several echocardiographic parameters can differentiate between normal and elevated LV filling pressure with good accuracy.In patients with heart failure and reduced EF (HFrEF), the main goal is to estimate LV filling pressures and grade the degree of diastolic dysfunction (diastolic dysfunction is presumed to be present in these patients) based on the parameters presented below and .
This guideline outlines a structured approach to the assessment of diastolic function and includes recommendations for the assessment of LV relaxation and filling pressures. Non-routine echocardiographic measures are described alongside guidance for application in .The term left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP) refers to the LV pressures during diastole. They are illustrated in Fig. 13.3 and include LV minimal pressure, pre-A wave pressure, and LV end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). Left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is a condition of impaired LV relaxation and increased LV chamber stiffness, which can lead to elevated LV filling pressures. This topic summarizes available echocardiographic methods for assessment of LV diastolic function. Values for average E/e′ ratio < 8 usually indicate normal LV filling pressures, values > 14 have high specificity for increased LV filling pressures. E/e′ ratio is not accurate in normal subjects, patients with heavy annular calcification, mitral valve and pericardial disease.
left ventricular filling pressure chart

increased left ventricular filling pressure
Ukraine moved into second place in Group C after a 3-1 win in Malta, while Hungary edged closer to securing qualification with a 2-2 draw in Lithuania
lv filling pressures|left ventricular filling pressure chart